Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a common yet often overlooked condition that affects the tissues surrounding your teeth. While many people focus on the impact periodontal disease has on their oral health, research has shown that this condition can also have significant implications for your overall well-being. In fact, gum disease has been linked to a variety of serious health issues, ranging from heart disease to diabetes and even Alzheimer’s disease. Understanding the connection between periodontal disease and overall health is crucial not only for your dental hygiene but for your general health as well.
What is Periodontal Disease?
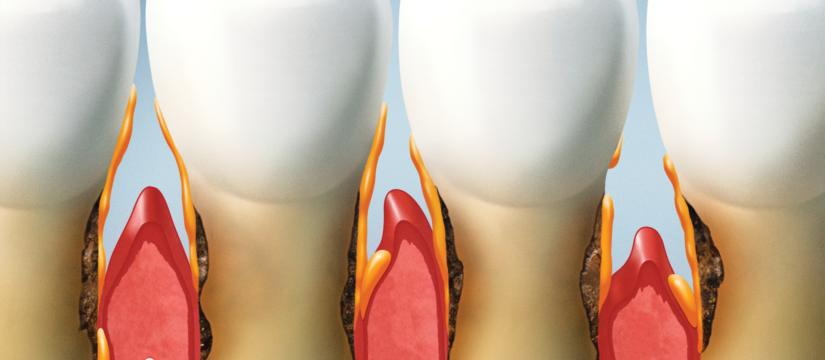
Periodontal disease is an infection of the tissues that hold your teeth in place. It typically starts as gingivitis, a mild form of gum disease that causes redness, swelling, and bleeding of the gums. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease where the infection spreads deeper into the tissues and can cause tooth loss.
The primary causes of periodontal disease include poor oral hygiene, smoking, genetics, certain medications, and conditions that affect the immune system. Factors like age, poor nutrition, and stress can also contribute to the development of periodontal disease. Regular dental checkups and good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing and flossing, are essential to preventing gum disease.
The Link Between Periodontal Disease and Heart Disease
One of the most significant connections between periodontal disease and overall health is the increased risk of heart disease. Studies have shown that people with gum disease are more likely to suffer from heart disease and other cardiovascular issues.
The bacteria from infected gums may enter the bloodstream, leading to an increased inflammatory response in the body. Chronic inflammation is a known risk factor for atherosclerosis (narrowing of the arteries), which can contribute to heart attacks, strokes, and other cardiovascular problems.
Diabetes and Periodontal Disease: A Two-Way Street
Diabetes and periodontal disease have a complex, bidirectional relationship. People with diabetes are more susceptible to gum disease because high blood sugar levels can weaken the immune system and make it harder for the body to fight infections, including gum infections.
The inflammation associated with gum disease can lead to higher blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of complications for people with diabetes. Research has shown that treating periodontal disease can improve blood sugar control in people with diabetes, further emphasizing the importance of maintaining good oral health in managing this chronic condition.
The Connection Between Periodontal Disease and Respiratory Health
There is also evidence to suggest that periodontal disease can contribute to respiratory problems. The bacteria from infected gums can be inhaled into the lungs, where they can cause or exacerbate respiratory conditions such as pneumonia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and even lung infections.
In fact, research has shown that individuals with gum disease are at a higher risk of developing pneumonia, especially if they are hospitalized or are living in long-term care facilities. Good oral hygiene and the treatment of periodontal disease may reduce the risk of developing respiratory infections and improve overall lung health.
Alzheimer’s Disease and Cognitive Decline
Emerging studies suggest a potential connection between periodontal disease and Alzheimer’s disease, as well as other forms of cognitive decline. While more research is needed to fully understand the relationship, studies have shown that people with periodontal disease may have a higher risk of developing Alzheimer’s or experiencing accelerated cognitive decline.
One theory is that the inflammation caused by gum disease may trigger an immune response that affects the brain. Additionally, the bacteria responsible for periodontal infections have been found in the brains of people with Alzheimer’s, suggesting that the bacteria may play a role in the development or progression of the disease.
Pregnancy and Periodontal Disease: Risks to Both Mother and Baby
Pregnant women are more susceptible to gum disease due to hormonal changes that increase the risk of inflammation and infection in the gums. Periodontal disease during pregnancy can increase the risk of complications such as preterm birth, low birth weight, and gestational diabetes. The inflammation caused by gum disease can trigger an immune response that affects the developing fetus.
Fortunately, treating gum disease during pregnancy can help reduce these risks. Regular dental visits, proper oral hygiene, and maintaining healthy gums during pregnancy are essential for both the mother and baby’s health.
Managing Periodontal Disease for Better Overall Health
The good news is that periodontal disease is preventable and treatable, and managing it can significantly reduce the risk of developing or worsening systemic health conditions. Here are some steps you can take to maintain healthy gums and overall well-being:
- Regular Dental Checkups: Seeing your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings is essential in detecting gum disease early and preventing it from progressing.
- Good Oral Hygiene Practices: Brushing twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antimicrobial mouthwash can help keep your gums healthy and free from infection.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking is a major risk factor for gum disease, so quitting can help improve both your oral health and overall health.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, particularly vitamin C and calcium, helps strengthen your immune system and support healthy gums.
- Manage Chronic Conditions: Keeping conditions like diabetes under control can help reduce the risk of developing gum disease and other related health issues.
- Seek Treatment Early: If you notice symptoms of gum disease, such as bleeding gums, bad breath, or swollen gums, seek treatment from a dentist as soon as possible to prevent further complications.
The link between periodontal disease and overall health is a reminder that oral health is not isolated to the mouth alone. Gum disease can impact many areas of your body, contributing to serious health conditions such as heart disease, diabetes, respiratory issues, cognitive decline, and complications during pregnancy. By prioritizing oral hygiene and seeking treatment for periodontal disease, you can improve not only your smile but also your overall health. Regular dental checkups and proper care are essential in maintaining a healthy mouth and a healthy body.
